The work environment is undergoing a significant transformation, largely driven by rapid technological advancements and shifting societal values. The Information Technology (IT) sector, known for its dynamic nature, is at the forefront of this evolution. A key element in this changing landscape is the rise of contingent IT talent — a group that includes freelancers, contractors, and consultants who offer their expertise to businesses on a non-permanent basis. Understanding the trends shaping this segment of the workforce is crucial for businesses and IT professionals alike to thrive in the future of work.
The contingent workforce has seen exponential growth in recent years, with more companies leveraging this flexible labor model to scale operations, access specialized skills, and drive innovation. For IT professionals, the shift towards contingent work offers unprecedented freedom and opportunities for career growth, but it also presents unique challenges in terms of job security, benefits, and professional development.
In this blog post, we delve into the key trends influencing the contingent IT talent landscape, explore the opportunities and challenges these trends present, and offer insights on how organizations and IT professionals can navigate this evolving terrain.
The Rise of Contingent IT Talent
The concept of contingent work is far from new, but its penetration into the IT sector has accelerated in recent years. Contingent IT workers, encompassing a diverse group of freelancers, independent contractors, and consultants, have become an integral part of the workforce for many organizations. This shift is underscored by compelling statistics: according to a report by Staffing Industry Analysts, the contingent workforce is projected to grow by 6% in 2024 alone, with IT roles leading the charge.
Defining Contingent IT TalentAt its core, contingent IT talent refers to professionals engaged by organizations on a non-permanent basis, typically to complete specific projects or fulfill temporary roles. Unlike traditional employees, these workers operate under fixed-term contracts, offering their skills and expertise in exchange for flexibility and often, higher pay rates.
Contingent IT talent can bring a range of specialized skills and domain expertise to organizations. From software developers and data analysts to cybersecurity specialists and project managers, these professionals contribute their knowledge and capabilities to address specific business needs. By tapping into this contingent talent pool, organizations can access a diverse range of skills and experiences, allowing for increased agility and rapid scaling of projects.
Growth DriversSeveral factors contribute to the growth of the contingent IT workforce:
Technological Advancements: Rapid innovation requires specialized skills that are often not available in-house. Contingent workers provide access to these niche skills on-demand. For example, organizations may engage contingent IT professionals with expertise in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, or cloud computing to drive digital transformation initiatives.
Need for Flexibility: Businesses face fluctuating demands and must adapt quickly to changing market conditions. Contingent IT talent allows companies to scale their workforce up or down without the overhead associated with permanent hires. This flexibility enables organizations to respond swiftly to project requirements, optimize resource allocation, and minimize costs during periods of lower demand.
Shift in Worker Preferences: The workforce is experiencing a significant shift in preferences, with more IT professionals seeking the autonomy, flexibility, and varied experiences that contingent work offers. This trend is especially prevalent among millennials and Gen Z individuals who prioritize work-life balance and value the freedom to choose projects that align with their interests and career goals.
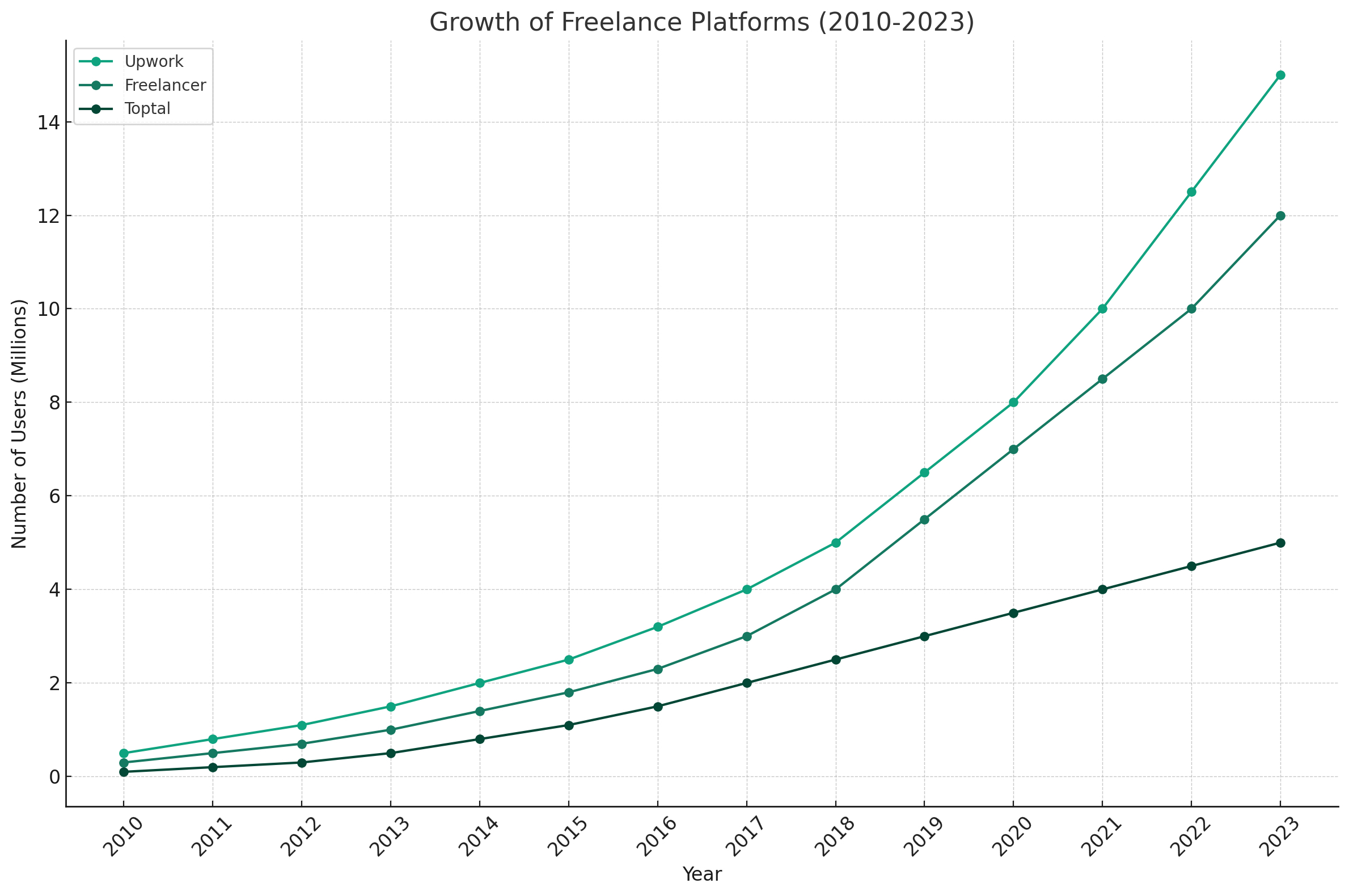
The rise of the gig economy and freelance platforms has further facilitated the growth of contingent work in the IT sector. Platforms like Upwork, Sourcer, Toptal, and Freelancer have created marketplaces that connect organizations with a vast talent pool of contingent IT professionals. These platforms offer transparency, convenience, and access to a global network of skilled individuals. Organizations can tap into these platforms to find professionals with the exact skills and experience required for their projects, while IT professionals can leverage these platforms to showcase their expertise and secure new opportunities.
Implications for Organizations and ProfessionalsThis shift towards contingent labor in the IT sector has profound implications for both organizations and professionals. Companies benefit from the agility and access to specialized skills that contingent IT talent brings. By engaging contingent workers, organizations can tap into a global talent pool, access niche expertise, and quickly scale their teams when needed. This flexibility allows organizations to adapt to market changes, launch new initiatives, and drive innovation.
On the other hand, IT professionals navigating the contingent IT talent landscape can enjoy greater control over their careers, the opportunity to work on diverse projects, and exposure to different industries and technologies. The contingent work model allows IT professionals to build a portfolio of experiences, develop a broader skill set, and explore various career paths. It also offers the potential for higher earning potential, as contingent workers often command higher rates due to their specialized skills and the flexibility they offer to organizations.
However, contingent work also presents unique challenges for both organizations and professionals. Organizations must carefully navigate issues related to compliance, legal obligations, and managing a blended workforce that includes permanent and contingent staff. Ensuring proper classification and adherence to employment laws is crucial to mitigate legal risks.
For IT professionals, the lack of job security and traditional employment benefits can be a concern. However, by strategically managing their careers, continuously upskilling, and building a strong professional network, IT professionals can thrive in the contingent IT talent landscape. They can leverage their expertise to secure exciting projects, command competitive rates, and build a reputation for delivering high-quality work.
Key Trends Influencing the Future of Work in IT
The contingent IT talent landscape is shaped by several key trends, each presenting new opportunities and challenges for organizations and professionals.
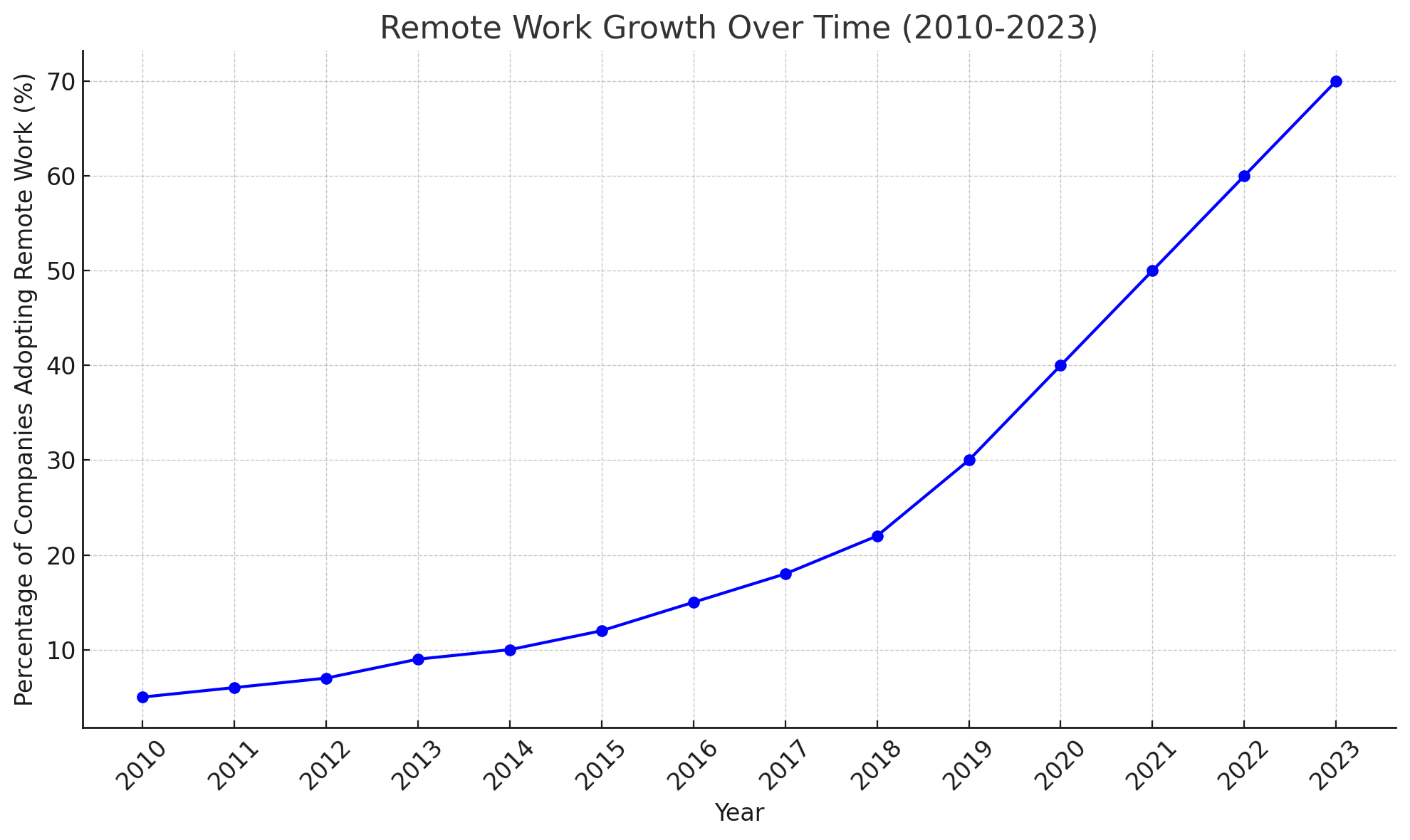
Remote Work and FlexibilityThe COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work, a trend that is particularly pronounced in the IT sector. This shift has had a profound impact on contingent IT talent. Remote work offers these professionals even greater flexibility, allowing them to collaborate with organizations globally regardless of geographic location. For companies, this means access to a broader talent pool and the ability to tap into the expertise of professionals who may not be available locally. Remote work has transformed the way organizations operate, emphasizing the need for effective communication, collaboration tools, and virtual project management platforms.
Artificial Intelligence and AutomationArtificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies are redefining the nature of work in the IT sector. Automation tools are increasingly capable of performing routine tasks, freeing up IT professionals to focus on higher-value activities. This shift has implications for both permanent and contingent IT workers.
For contingent IT talent, staying ahead means continually upskilling and adapting to these technological shifts. Professionals need to develop expertise in areas that complement and enhance AI and automation technologies. For example, AI developers, data scientists, and cybersecurity specialists will continue to be in high demand. Organizations looking to engage contingent IT talent can prioritize professionals skilled in cutting-edge technologies to drive innovation and optimize business processes.
Gig Economy and Freelance PlatformsThe gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, continues to grow in the IT sector. Freelance platforms have played a significant role in facilitating the connection between organizations and contingent IT professionals. Platforms like Upwork, Sourcer, and Toptal provide an avenue for organizations to access a vast talent pool and find professionals with the specific skills and expertise required for their projects.
For IT professionals, these platforms offer an opportunity to showcase their expertise, build a reputation, and secure new projects. However, the gig economy also introduces a competitive landscape where professionals must distinguish themselves. Building a strong personal brand, highlighting relevant experience and skills, and providing exceptional service are critical for success in the gig economy.
In the rapidly evolving IT sector, continuous learning is non-negotiable. Technology is advancing at an unprecedented pace, necessitating constant upskilling to stay relevant in the job market. This trend is particularly relevant for contingent IT professionals who must showcase their expertise and adapt to the changing needs of organizations.
IT professionals should prioritize upskilling in emerging technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and data analytics. Certifications and training programs can help professionals demonstrate their knowledge and expertise to potential employers. Continuous learning also helps IT professionals stay abreast of industry trends, enabling them to offer the most relevant and up-to-date solutions to organizations.
Organizations, too, need to prioritize upskilling and professional development for their contingent IT workers. By investing in the growth and development of their contingent workforce, organizations can ensure that they have access to the latest skills and expertise required to meet business objectives.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) InitiativesDiversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) have gained significant importance in the workplace. Organizations are recognizing the value of a diverse workforce and the positive impact it has on innovation, creativity, and problem-solving. The contingent IT talent landscape offers an opportunity for organizations to embrace diversity and tap into a wider range of skills, experiences, and perspectives.
By actively engaging a diverse pool of contingent IT professionals, organizations can drive innovation and foster a culture of inclusion. This can be achieved by implementing inclusive talent acquisition practices, promoting equal opportunities for all professionals, and creating a supportive work environment that values diversity.
Embracing DEI initiatives in the contingent IT talent landscape requires organizations to examine their hiring practices, ensure equal access to opportunities, and foster a culture of respect and inclusion. By doing so, organizations can attract and retain top-tier contingent IT talent, foster innovation, and drive business success.
These trends underscore the dynamic nature of the contingent IT talent landscape, highlighting the need for both organizations and professionals to remain adaptable, proactive, and strategic in their approach to the future of work. By embracing these trends and preparing strategically, organizations can tap into a diverse talent pool, drive innovation, and adapt to changing market needs. IT professionals, on the other hand, can seize opportunities for career growth, leverage their expertise, and enjoy the flexibility and autonomy that contingent work offers.
Challenges Facing Contingent IT Talent
While the contingent IT workforce model offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that both professionals and organizations need to navigate carefully.
Job Security and BenefitsOne of the most significant concerns for contingent IT workers is the inherent lack of job security and traditional employment benefits. Unlike their counterparts in permanent roles, contingent workers often face uncertainties regarding their next project or contract, and may not have access to health insurance, retirement plans, or paid leave.
Strategies for Mitigation:
For Professionals: Building a strong personal brand, networking effectively, and continuously upskilling can help secure a steady stream of opportunities. By actively cultivating a strong professional network, professionals can increase their chances of receiving referrals and finding new projects. Additionally, investing in professional development and acquiring in-demand skills can make professionals more marketable and sought-after by organizations.
For Organizations: Offering competitive rates, performance-based bonuses, and access to professional development resources can make contingent roles more attractive to skilled IT professionals. Organizations should also consider providing access to benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, which can help attract and retain top talent within the contingent workforce.
Contingent workers may struggle with feeling disconnected from the company culture and team dynamics, given their temporary status and potential remote working conditions. This can impact team cohesion, collaboration, and ultimately, project outcomes.
Strategies for Integration:
For Organizations: Engaging contingent IT talent in team-building activities, providing clear communication about company values and goals, and involving them in decision-making processes can foster a sense of belonging. Regular check-ins and virtual meetings can help bridge the gap between permanent and contingent team members. Leveraging collaboration tools and project management platforms can also facilitate seamless integration and communication.
For Professionals: Taking initiative to participate in company and team events, and making an effort to connect with coworkers can help bridge the gap. Contributing actively to team discussions, sharing knowledge and expertise, and seeking opportunities to collaborate can enhance integration and demonstrate commitment to the project and team success.
Navigating the legal landscape of contingent work can be complex for both organizations and professionals. Potential challenges include misclassification of employees, compliance with labor laws across different jurisdictions, and managing contractual obligations.
Best Practices:
For Organizations: Seeking legal counsel to ensure compliance with employment laws and regulations is crucial. Organizations should carefully classify workers to avoid misclassification issues and related legal ramifications. By implementing standardized processes for engaging and managing contingent workers, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure compliance.
For Professionals: Staying informed about the legal rights and obligations related to contingent work is essential. Professionals should seek contracts that clearly define terms of engagement, compensation, and scope of work. Familiarizing themselves with relevant employment laws in their respective jurisdictions can also help professionals protect their rights.
Preparing for the Future: Strategies for Organizations and IT Professionals
To thrive in the evolving landscape of contingent IT talent, both organizations and professionals must adopt strategic approaches.
For OrganizationsAttract and Retain Top IT Talent: Offering competitive compensation, opportunities for professional development, and meaningful project work can attract top contingent IT talent. Emphasizing the value proposition of working with the organization, such as exciting projects, access to cutting-edge technologies, and opportunities for career growth, can help organizations stand out in a competitive market.
Invest in Technology and Infrastructure: Providing the necessary tools and platforms that support collaboration, communication, and productivity is essential. Organizations should invest in project management tools, virtual collaboration platforms, and secure remote access solutions to facilitate seamless integration of contingent IT talent into project teams.
Strategic Workforce Planning: Leveraging data and analytics to forecast talent needs and develop a balanced mix of permanent and contingent IT talent can ensure agility, cost-effectiveness, and long-term success. Organizations should identify key skills and expertise required for their projects and establish relationships with trusted staffing agencies or freelance platforms to access the right talent at the right time.
Skills Development and Certification: Pursuing certifications and training in high-demand areas of the IT industry can enhance employability and increase market value. IT professionals should continuously upskill and stay informed about emerging technologies and industry trends. By investing in their own professional development, professionals can position themselves as experts in their respective fields and open doors to exciting opportunities within the contingent IT talent landscape.
Networking and Personal Branding: Building a strong professional network can significantly impact career opportunities within the contingent IT talent landscape. Professionals should engage in industry events, join online communities, and actively participate in relevant discussions. Building a personal brand through thought leadership, blogging, and social media presence can help professionals gain visibility and attract potential clients or employers.
Navigating the Freelance Marketplace: Success in the freelance marketplace requires careful positioning and effective self-marketing. Professionals should create a compelling profile that highlights their skills, expertise, and past accomplishments. They should also proactively seek out relevant projects, submit well-crafted proposals, and maintain a strong online presence. Excellent communication skills and a track record of delivering quality work on time are crucial to securing repeat business and building a positive reputation.
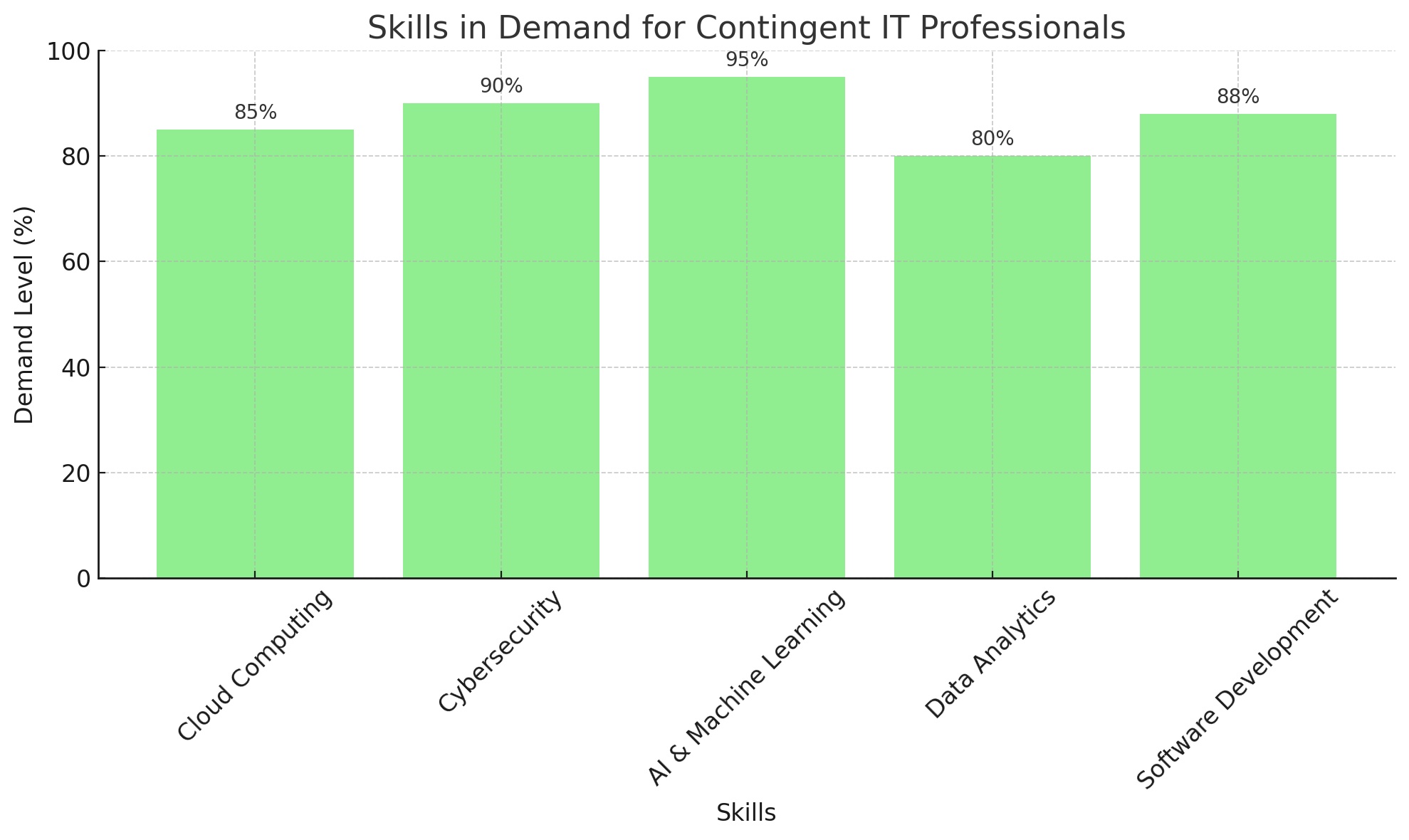
The Role of HR and Talent Acquisition in Shaping the Contingent IT Talent Landscape
Human Resources (HR) and Talent Acquisition teams play a pivotal role in strategically integrating contingent IT talent into the workforce.
Best practices for sourcing and managing contingent IT workers include leveraging specialized staffing agencies, using freelance platforms effectively, and developing clear policies for contingent worker engagement. Organizations should establish strong relationships with reputable staffing agencies and freelance platforms that align with their specific needs. Effectively communicating project requirements, ensuring proper onboarding, and providing ongoing support and feedback are essential for successfully integrating contingent IT talent.
Strategic workforce planning is crucial for determining the optimal mix of permanent and contingent talent based on project needs, business goals, and budget considerations. HR teams should collaborate with hiring managers, project leads, and other stakeholders to identify skill gaps and forecast future talent requirements. By understanding the organization's short-term and long-term goals, HR teams can develop strategies for attracting, engaging, and retaining the right mix of contingent IT talent.
Leveraging technology for efficient talent acquisition and management can streamline processes and enhance compliance. Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) can help manage the end-to-end recruitment process, from job posting to candidate selection. Vendor Management Systems (VMS) can streamline the engagement and management of contingent workers, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Embracing innovative HR tech solutions can improve efficiency, reduce administrative burden, and enable HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Conclusion
The contingent IT talent landscape is characterized by both exciting opportunities and notable challenges. As we look towards the future of work, it's evident that flexibility, continuous learning, and strategic workforce planning will be key themes. By embracing these trends and preparing strategically, both organizations and IT professionals can navigate this dynamic environment successfully, unlocking the full potential of contingent work in the IT sector. The journey requires adaptation, proactive talent management, continuous learning, and strategic planning, but the rewards — in terms of agility, access to specialized skills, and career growth — are substantial.
In conclusion, the future of work in the IT sector is being shaped by various trends, with the rise of contingent IT talent playing a prominent role. As organizations adapt to the changing dynamics of the workforce, contingent IT professionals offer valuable skills, expertise, and flexibility. However, this shift also presents challenges that need to be addressed by both organizations and professionals.
Organizations must strive to create an inclusive and supportive work environment that integrates contingent IT talent seamlessly. This includes providing opportunities for professional development, fostering a sense of belonging, and addressing concerns around job security and benefits. Strategic workforce planning, investment in technology and infrastructure, and adherence to compliance requirements are critical for organizations to effectively leverage the contingent IT talent pool.
For IT professionals, embracing the contingent work model requires continuous upskilling, networking, and personal branding. By positioning themselves as experts and staying current with industry trends, professionals can stay competitive in the gig economy and secure rewarding projects. Navigating the freelance marketplace and effectively managing relationships with clients or employers are key skills for success.
Furthermore, HR and Talent Acquisition teams play a vital role in shaping the contingent IT talent landscape. By implementing best practices for sourcing, engaging, and managing contingent workers, HR teams can facilitate the integration of these professionals into project teams. Leveraging technology, such as Vendor Management Systems and Applicant Tracking Systems, can streamline processes and ensure compliance.
Overall, the contingent IT talent landscape presents immense opportunities for organizations and professionals. By embracing the trends shaping the future of work, managing the associated challenges, and adopting proactive strategies, both organizations and professionals can thrive in this dynamic landscape. The key lies in staying adaptable, continuously learning, and strategically aligning talent with business objectives. By doing so, organizations can access a diverse pool of skills, drive innovation, and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving IT industry, while IT professionals can enjoy flexibility, career growth, and exciting project opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To provide further clarity on the topic of contingent IT talent and the future of work, let's address some frequently asked questions.
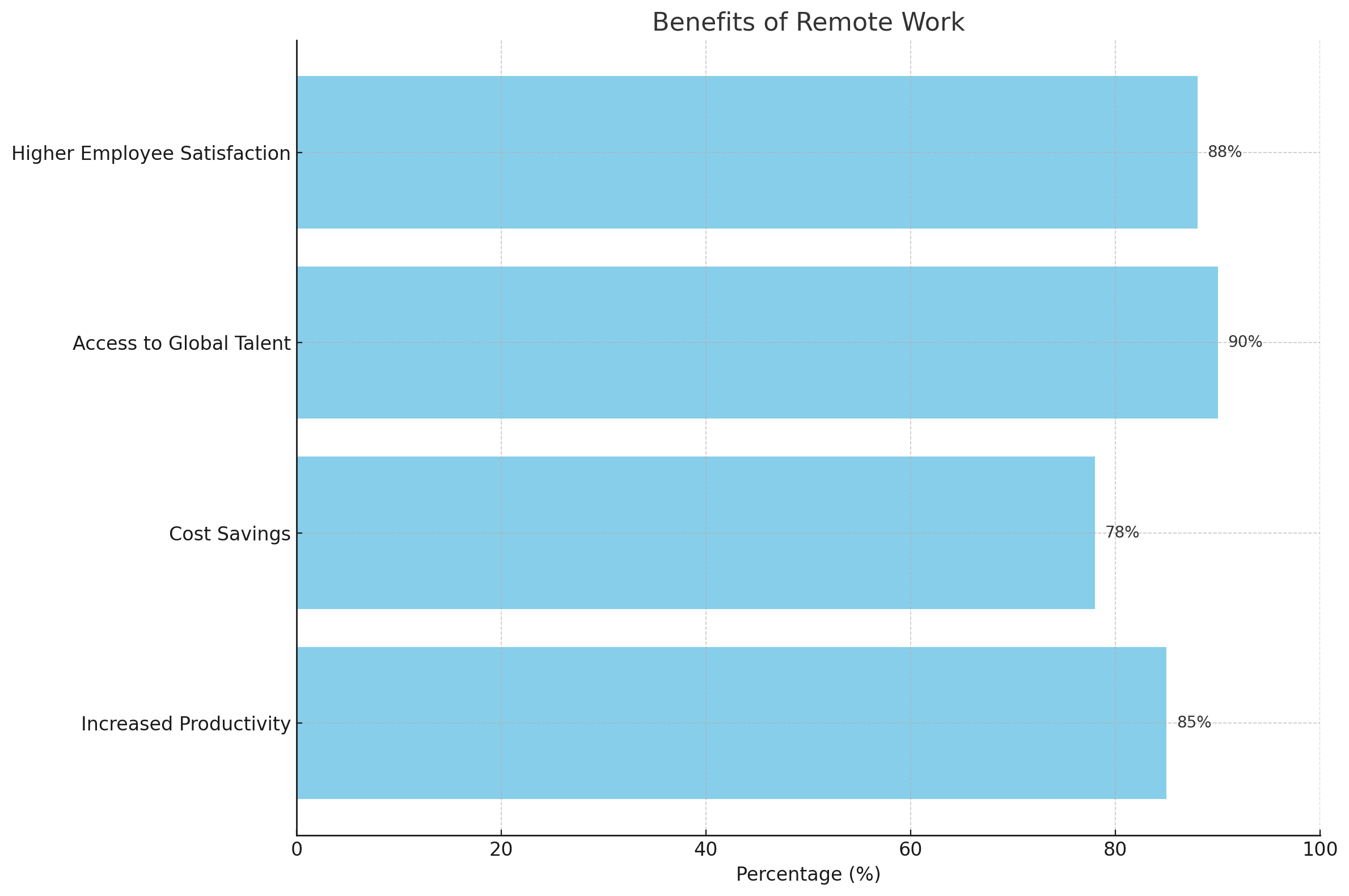
What are the benefits of hiring contingent IT talent?Hiring contingent IT talent offers several benefits, including:
- Access to specialized skills: Contingent IT professionals bring niche expertise and can quickly fill skill gaps.
- Flexibility: Organizations can scale their workforce up or down based on project needs.
- Cost savings: Hiring contingent talent can be more cost-effective than maintaining a full-time workforce.
- Innovation and fresh perspectives: Contingent workers bring diverse experiences and ideas to the table.
- Agility: Organizations can quickly adapt to changing market conditions by leveraging contingent talent.
To ensure the quality of work from contingent IT professionals, organizations can:
- Thoroughly vet and interview candidates before engaging them.
- Seek recommendations and referrals from trusted sources.
- Clearly communicate project expectations and deliverables.
- Establish regular checkpoints and feedback mechanisms.
- Provide access to necessary resources, tools, and support.
Contingent IT professionals can differentiate themselves by:
- Cultivating a strong personal brand through online presence and thought leadership.
- Showcasing their expertise and past successes through a well-curated portfolio.
- Networking with industry professionals and seeking referrals.
- Continuously upskilling and staying updated on industry trends.
- Providing excellent communication, reliability, and responsiveness to clients.
To foster collaboration between permanent and contingent IT workers, organizations can:
- Establish clear communication channels and project management frameworks.
- Encourage regular team meetings and virtual social activities.
- Involve contingent workers in decision-making processes.
- Provide opportunities for knowledge sharing and cross-training.
- Foster a culture of inclusivity and appreciation for different perspectives.
Managing a blended workforce requires organizations to:
- Develop clear policies and guidelines for engaging contingent workers.
- Implement technology solutions to streamline talent acquisition and management processes.
- Foster a culture of collaboration and mutual respect among all team members.
- Provide access to training and development opportunities for both permanent and contingent staff.
- Regularly assess and adjust workforce strategies based on project needs and business goals.